A closer look at U.S. deaths due to COVID-19
By YANNI GU | November 22, 2020
This article originally published at:
https://www.jhunewsletter.com/article/2020/11/a-closer-look-at-u-s-deaths-due-to-covid-19
COURTESY OF GENEVIEVE BRIAND
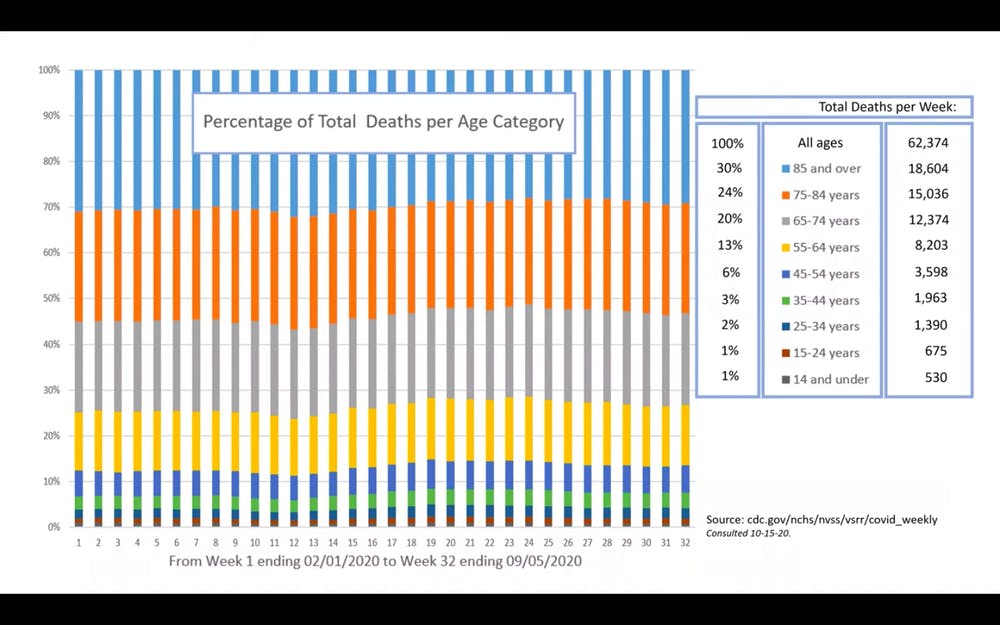
After retrieving data on the CDC website, Briand compiled a graph representing percentages of total deaths per age category from early February to early September.
According to new data, the U.S. currently ranks first in total COVID-19 cases, new cases per day and deaths. Genevieve Briand, assistant program director of the Applied Economics master’s degree program at Hopkins, critically analyzed the effect of COVID-19 on U.S. deaths using data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in her webinar titled “COVID-19 Deaths: A Look at U.S. Data.”
From mid-March to mid-September, U.S. total deaths have reached 1.7 million, of which 200,000, or 12% of total deaths, are COVID-19-related. Instead of looking directly at COVID-19 deaths, Briand focused on total deaths per age group and per cause of death in the U.S. and used this information to shed light on the effects of COVID-19.
She explained that the significance of COVID-19 on U.S. deaths can be fully understood only through comparison to the number of total deaths in the United States.
After retrieving data on the CDC website, Briand compiled a graph representing percentages of total deaths per age category from early February to early September, which includes the period from before COVID-19 was detected in the U.S. to after infection rates soared.
Surprisingly, the deaths of older people stayed the same before and after COVID-19. Since COVID-19 mainly affects the elderly, experts expected an increase in the percentage of deaths in older age groups. However, this increase is not seen from the CDC data. In fact, the percentages of deaths among all age groups remain relatively the same.
“The reason we have a higher number of reported COVID-19 deaths among older individuals than younger individuals is simply because every day in the U.S. older individuals die in higher numbers than younger individuals,” Briand said.
Briand also noted that 50,000 to 70,000 deaths are seen both before and after COVID-19, indicating that this number of deaths was normal long before COVID-19 emerged. Therefore, according to Briand, not only has COVID-19 had no effect on the percentage of deaths of older people, but it has also not increased the total number of deaths.
These data analyses suggest that in contrast to most people’s assumptions, the number of deaths by COVID-19 is not alarming. In fact, it has relatively no effect on deaths in the United States.
This comes as a shock to many people. How is it that the data lie so far from our perception?
To answer that question, Briand shifted her focus to the deaths per causes ranging from 2014 to 2020. There is a sudden increase in deaths in 2020 due to COVID-19. This is no surprise because COVID-19 emerged in the U.S. in early 2020, and thus COVID-19-related deaths increased drastically afterward.
Analysis of deaths per cause in 2018 revealed that the pattern of seasonal increase in the total number of deaths is a result of the rise in deaths by all causes, with the top three being heart disease, respiratory diseases, influenza and pneumonia.
“This is true every year. Every year in the U.S. when we observe the seasonal ups and downs, we have an increase of deaths due to all causes,” Briand pointed out.
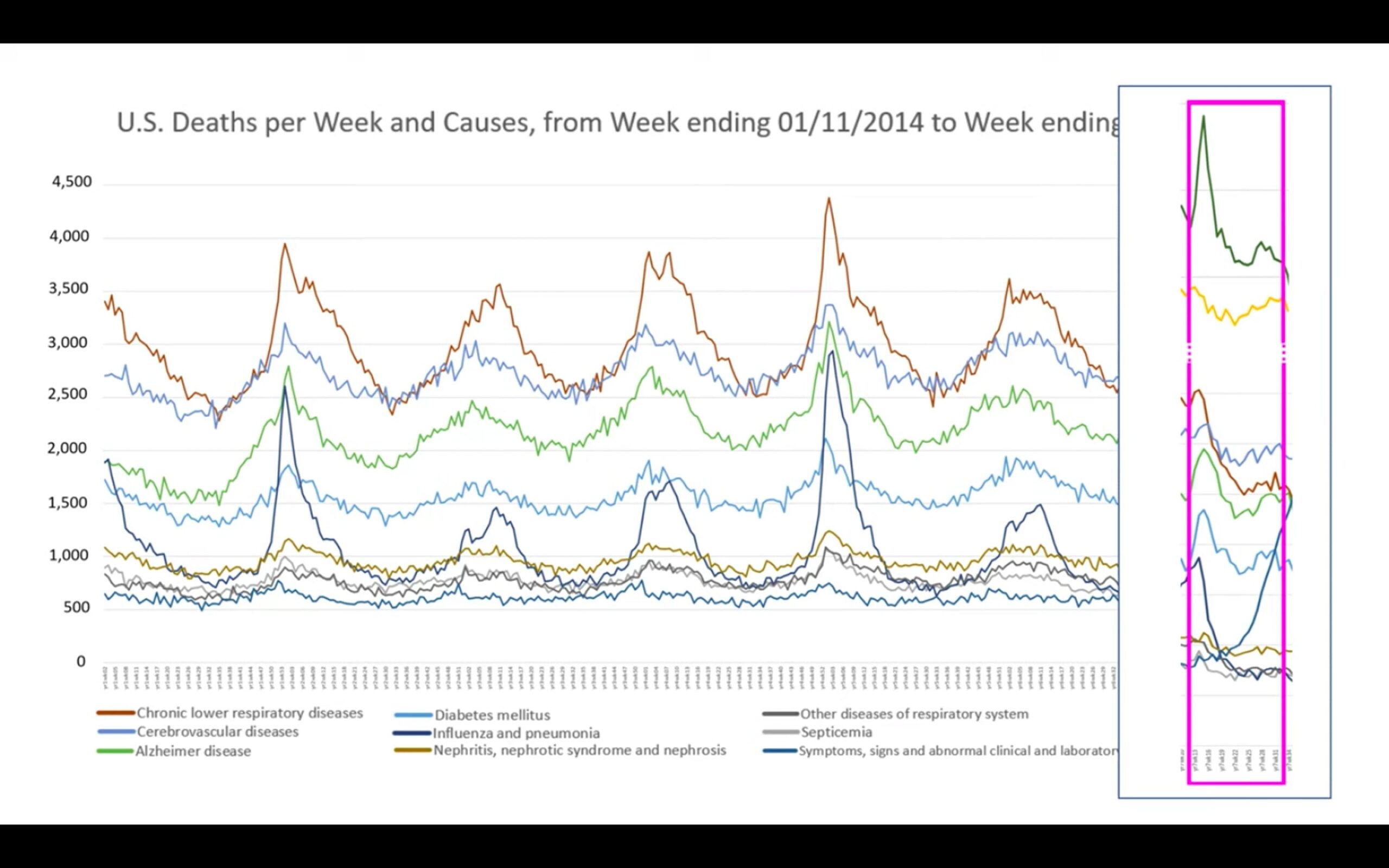
When Briand looked at the 2020 data during that seasonal period, COVID-19-related deaths exceeded deaths from heart diseases. This was highly unusual since heart disease has always prevailed as the leading cause of deaths. However, when taking a closer look at the death numbers, she noted something strange. As Briand compared the number of deaths per cause during that period in 2020 to 2018, she noticed that instead of the expected drastic increase across all causes, there was a significant decrease in deaths due to heart disease. Even more surprising, as seen in the graph below, this sudden decline in deaths is observed for all other causes.
COURTESY OF GENEVIEVE BRIAND
Graph depicts the number of deaths per cause during that period in 2020 to 2018.
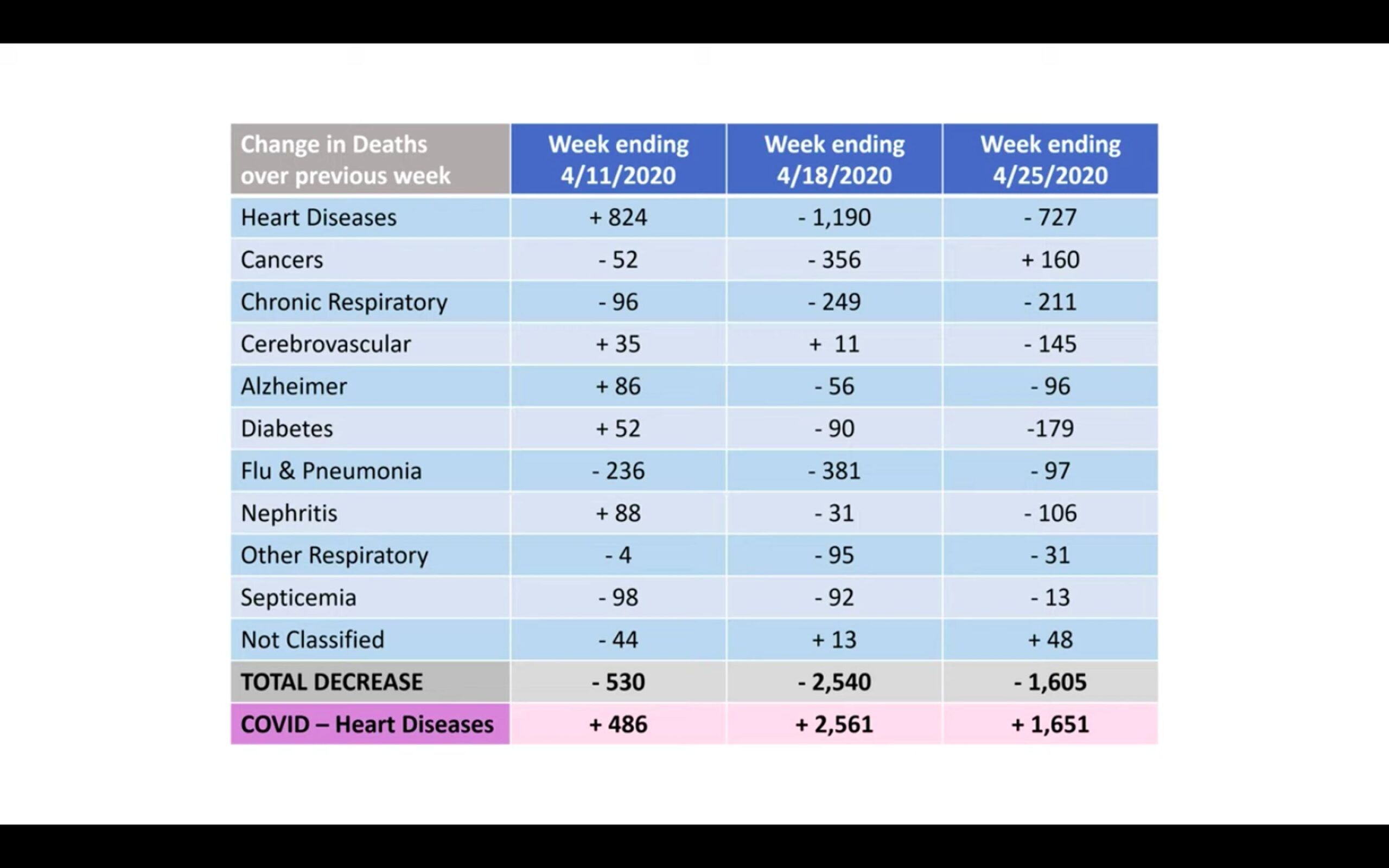
This trend is completely contrary to the pattern observed in all previous years. Interestingly, as depicted in the table below, the total decrease in deaths by other causes almost exactly equals the increase in deaths by COVID-19. This suggests, according to Briand, that the COVID-19 death toll is misleading. Briand believes that deaths due to heart diseases, respiratory diseases, influenza and pneumonia may instead be recategorized as being due to COVID-19.
COURTESY OF GENEVIEVE BRIAND
Graph depicts the total decrease in deaths by various causes, including COVID-19.
The CDC classified all deaths that are related to COVID-19 simply as COVID-19 deaths. Even patients dying from other underlying diseases but are infected with COVID-19 count as COVID-19 deaths. This is likely the main explanation as to why COVID-19 deaths drastically increased while deaths by all other diseases experienced a significant decrease.
“All of this points to no evidence that COVID-19 created any excess deaths. Total death numbers are not above normal death numbers. We found no evidence to the contrary,” Briand concluded.
In an interview with The News-Letter, Briand addressed the question of whether COVID-19 deaths can be called misleading since the infection might have exacerbated and even led to deaths by other underlying diseases.
“If [the COVID-19 death toll] was not misleading at all, what we should have observed is an increased number of heart attacks and increased COVID-19 numbers. But a decreased number of heart attacks and all the other death causes doesn’t give us a choice but to point to some misclassification,” Briand replied.
In other words, the effect of COVID-19 on deaths in the U.S. is considered problematic only when it increases the total number of deaths or the true death burden by a significant amount in addition to the expected deaths by other causes. Since the crude number of total deaths by all causes before and after COVID-19 has stayed the same, one can hardly say, in Briand’s view, that COVID-19 deaths are concerning.
Briand also mentioned that more research and data are needed to truly decipher the effect of COVID-19 on deaths in the United States.
Throughout the talk, Briand constantly emphasized that although COVID-19 is a serious national and global problem, she also stressed that society should never lose focus of the bigger picture — death in general.
The death of a loved one, from COVID-19 or from other causes, is always tragic, Briand explained. Each life is equally important and we should be reminded that even during a global pandemic we should not forget about the tragic loss of lives from other causes.
According to Briand, the over-exaggeration of the COVID-19 death number may be due to the constant emphasis on COVID-19-related deaths and the habitual overlooking of deaths by other natural causes in society.
During an interview with The News-Letter after the event, Poorna Dharmasena, a master’s candidate in Applied Economics, expressed his opinion about Briand’s concluding remarks.
“At the end of the day, it’s still a deadly virus. And over-exaggeration or not, to a certain degree, is irrelevant,” Dharmasena said.
When asked whether the public should be informed about this exaggeration in death numbers, Dharmasena stated that people have a right to know the truth. However, COVID-19 should still continuously be treated as a deadly disease to safeguard the vulnerable population.